Introduction
Knee bursitis is a painful condition that can limit your ability to move freely and comfortably. It occurs when the bursae—small fluid-filled sacs that cushion your knee joint—become inflamed. Whether caused by repetitive movements, prolonged kneeling, or an injury, knee bursitis can significantly affect your daily life.
If you’re experiencing knee bursitis and looking for effective treatment, ONI Physio Fitness is here to help. Based in Mont Kiara, Kuala Lumpur, and catering to nearby areas like Sri Hartamas and Petaling Jaya, we provide expert physiotherapy solutions to alleviate pain, restore mobility, and prevent recurrence.
What Is Knee Bursitis?
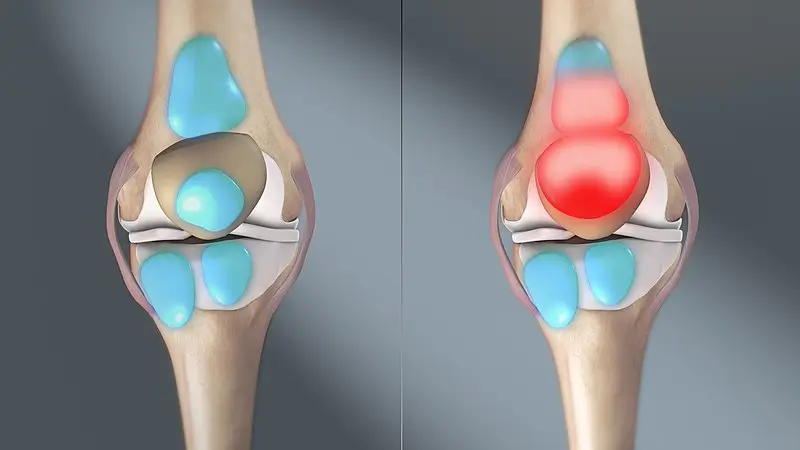
Knee bursitis is the inflammation of the bursae around the knee joint. These bursae act as cushions to reduce friction between bones, tendons, and muscles. When they become irritated or overused, they can swell, leading to pain and restricted movement.
The condition most commonly affects the prepatellar bursa (in front of the kneecap) and the infrapatellar bursa (below the kneecap), but other bursae in the knee can also be affected.
What Causes Knee Bursitis?
Several factors can lead to knee bursitis, including:
- Prolonged Kneeling: Occupations like gardening, cleaning, or tiling put pressure on the kneecap.
- Repetitive Movements: Activities involving frequent bending or squatting can irritate the bursae.
- Trauma or Injury: A direct impact to the knee can cause bursae inflammation.
- Infections: In rare cases, an infected bursa can lead to septic bursitis.
- Underlying Conditions: Conditions like arthritis or gout may increase the risk of bursitis.
Symptoms of Knee Bursitis
The most common symptoms of knee bursitis include:
- Localized Swelling: A noticeable bump or puffiness around the affected bursa.
- Pain: Discomfort that worsens with movement or pressure.
- Warmth and Redness: These symptoms may indicate inflammation or infection.
- Limited Range of Motion: Stiffness in the knee, making it hard to bend or straighten fully.
- Tenderness: Painful to touch, especially over the inflamed bursa.
Common Populations Affected by Knee Bursitis
Certain groups are more prone to developing knee bursitis:
- Athletes: Sports like wrestling, basketball, and volleyball involve frequent knee impacts.
- Manual Laborers: Jobs that require prolonged kneeling or squatting.
- Older Adults: Age-related changes in joint structures can increase susceptibility.
- People with Preexisting Conditions: Those with arthritis, gout, or diabetes are at higher risk.
Knee Bursitis Treatment
Knee bursitis treatment aims to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and restore mobility. Here’s a breakdown of common approaches:
1. Rest and Activity Modification
Avoid activities that aggravate your symptoms.
Use knee pads or cushions to protect your knees if kneeling is unavoidable.
2. Ice and Compression
Apply an ice pack to the affected area for 15–20 minutes every few hours to reduce swelling.
Use a compression wrap to limit further swelling.
3. Medication
Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen can help manage pain and swelling.
Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in both acute and long-term recovery. At ONI Physio Fitness, we:
Use manual therapy to relieve stiffness and tension around the knee.
Provide a personalized rehabilitation plan with strengthening and stretching exercises.
Guide you on safe movements and techniques to prevent recurrence.
5. Aspiration or Injections
In severe cases, fluid may need to be drained from the bursa, or corticosteroid injections may be administered by a doctor.
Exercises for Knee Bursitis
Below are three physiotherapist-approved exercises to aid in recovery from knee bursitis. Always consult a professional before starting any exercise routine.
Straight Leg Raise
- Lie on your back with one leg bent and the other straight.
- Tighten your thigh muscles and lift the straight leg to about 12 inches off the ground.
- Hold for 3–5 seconds, then lower it slowly.
- Repeat 10–12 times per leg, 2–3 times daily.
Quad Stretch
- Stand upright and hold onto a wall or chair for balance.
- Bend one knee and grab your ankle, pulling it toward your buttocks.
- Keep your knees close together and avoid arching your back.
- Hold for 20–30 seconds per leg, repeating 2–3 times per session.
Hamstring Stretch
- Sit on the floor with one leg extended and the other bent inward.
- Lean forward from your hips, keeping your back straight, and reach toward your toes.
- Hold the stretch for 20–30 seconds and repeat 3 times per leg.
Prevention of Knee Bursitis
Preventing knee bursitis involves minimizing stress on your joints and maintaining good knee health:
- Use Knee Protection: Wear knee pads or cushions during activities that require prolonged kneeling.
- Strengthen Supporting Muscles: Build strong quadriceps and hamstrings to support the knee.
- Stretch Regularly: Stretching helps improve flexibility and reduce strain on the bursae.
- Warm Up Before Exercise: Prepare your muscles and joints with a proper warm-up routine.
- Modify Activities: Avoid repetitive movements or take frequent breaks when engaging in high-impact activities.
Conclusion
Knee bursitis can be painful and disruptive, but with the right treatment and preventive measures, you can regain your mobility and comfort. ONI Physio Fitness in Mont Kiara, Kuala Lumpur, offers expert physiotherapy services to treat knee bursitis effectively.
Don’t let knee pain hold you back—book your appointment with ONI Physio Fitness today and take the first step toward a pain-free life!